 Image credit: Unsplash
Image credit: Unsplash
Abstract
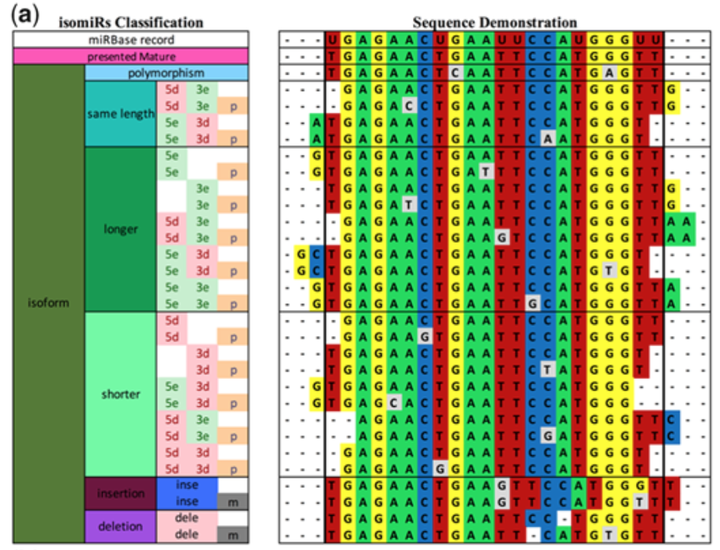
The existence of complex subpopulations of miRNA isoforms, or isomiRs, is well established. While many tools exist for investigating isomiR populations, they differ in how they characterize an isomiR, making it difficult to compare results across different tools. Thus, there is a need for a more comprehensive and systematic standard for defining isomiRs. Such a standard would allow investigation of isomiR population structure in progressively more refined sub-populations, permitting the identification of more subtle changes between conditions and leading to an improved understanding of the processes that generate these differences. We developed Jasmine, a software tool that incorporates a hierarchal framework for characterizing isomiR populations. Jasmine is a Java application that can process raw read data in fastq/fasta format, or mapped reads in SAM format to produce a detailed characterization of isomiR populations. Thus, Jasmine can reveal structure not apparent in a standard miRNA-Seq analysis pipeline.