Identification and BAC construction of Han, the first characterized HCMV clinical strain in China
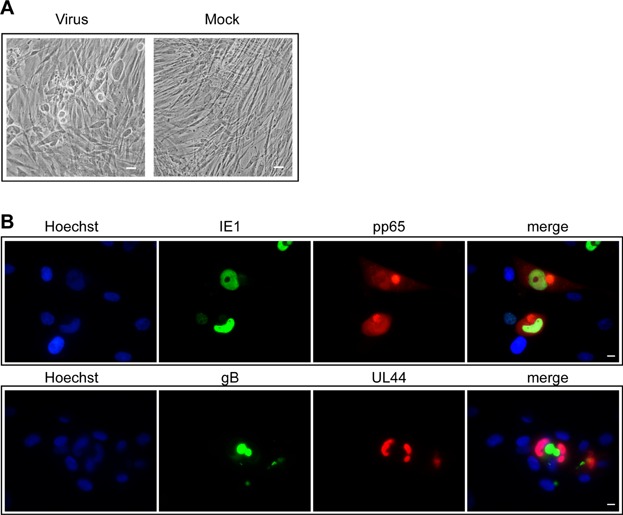 Image credit: Unsplash
Image credit: Unsplash
Abstract
Human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) is the leading infectious cause of birth defects, and may lead to severe or lethal diseases in immunocompromised individuals. Several HCMV strains have been identified and widely applied in research, but no isolate from China has been characterized. In the present study, we isolated, characterized and sequenced the first Chinese HCMV clinical strain Han, and constructed the novel and functional HCMV infectious clone Han‐BAC‐2311. HCMV Han was isolated from the urine sample of a Chinese infant with multiple developmental disorders. It expresses HCMV specific proteins and contains a representative HCMV genome with minor differences compared to other strains. By homologous recombination using mini‐F derived BAC vector pUS‐F6, the infectious clone Han‐BAC‐2311 was constructed containing representative viral genes across the HCMV genome. The insertion site and orientation of BAC sequence were confirmed by restriction enzyme digestion and Southern blotting. The reconstituted recombinant virus HanBAC‐2311 expresses typical viral proteins with the same pattern as that of wild‐type Han, and also displayed a similar growth kinetics to wild‐type Han. The identification of the first clinical HCMV strain in China and the construction of its infectious clone will greatly facilitate the pathogenesis studies and vaccine development.